- electric charge
- pos and neg
- pos == proton
- neg == electron
- Proton mas >>>> electron
- Proton charge == electron
- neutron no charge > proton
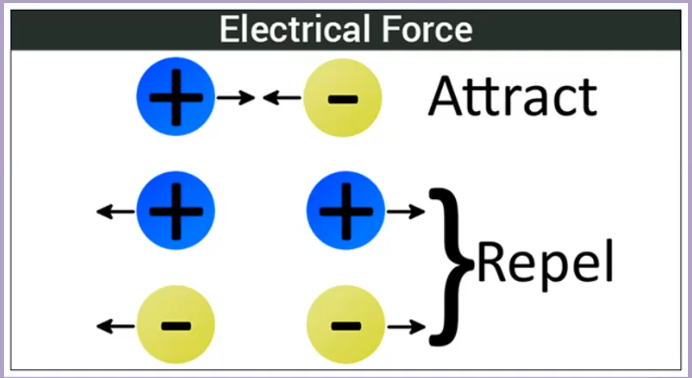
- Electrical Forces
- Conservation of Charge
- Neutral means equal protons and electrons
- If inequal, not neutral
- charged atom is called ion
- charge not destroyed, it is transferred/changed
- Coulomb's Law
- The electrical force decreases inversly to distance
- Like gravity
- Conductors
- Like heat
- conductor of electrical current
- same reason for good heat
- if electrons aren't free, its bad
- 1-2 valence electrons
- Insulator
- Electrons aren;t free
- doesn't conduct current well
- 5-6 valence electrons
- SemiConductors
- depends of temperature
- silicon is neither
- can be made to behave as either
- Charging
- Friction
- causes heat and frees electrons
- easier current and loose electrons
- Balloon example
- Contact
- Charges transfer until equilibrium
- very positive/negative can take away electrons/protons
- Touching doorknob
- Induction
- repelling other type of electron can sort and charge
-
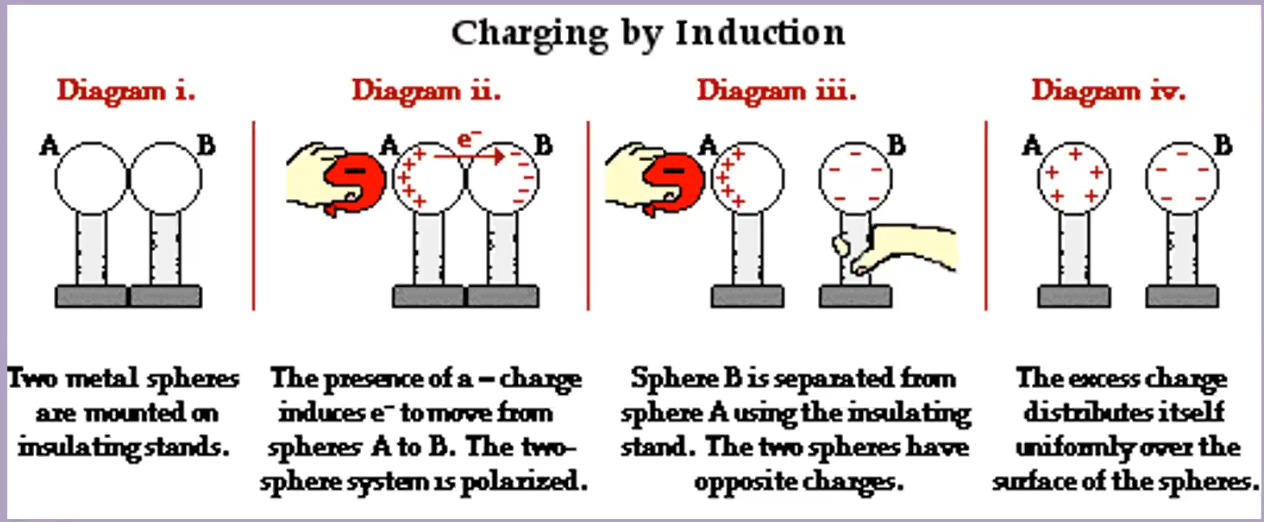
- neutral => charged
- Electric Field
- Like grav force
- Mass is charge instead
- like a grav field, it is in space
- Pos charge
- Neg charge
- Coulombs
- Example
- Electric Potential
- Like pulling 2 magnets apart
- same way for Grav PE